I. Team Overview
Starting from the practical needs of rail transit operations, the research team focuses on traffic safety inspection and system fault diagnosis.
Leveraging machine vision technologies and integrating deep learning theories and methodologies, the team conducts automated identification of defects or damages in rail transit infrastructure—including track structures and catenary systems—as well as critical equipment components. Additionally, based on vibration signal analysis and employing advanced signal processing techniques combined with deep learning, the team carries out research on fault diagnosis and prognostics for rail transit equipment and systems. This includes reliability analysis, failure mechanism investigation, service capability assessment, remaining useful life prediction, and optimization of maintenance strategies—thereby contributing significantly to the intelligent advancement of rail transit inspection technologies. By fusing machine vision with deep learning, the team has conducted in-depth research and successfully developed highly efficient and accurate online inspection systems for tracks and pantographs. These systems enable automated detection and evaluation of key components such as rail fasteners, rail surface conditions, and pantograph defects, substantially improving both inspection efficiency and accuracy. Furthermore, by applying advanced signal processing and deep learning theories, the team has developed fault diagnosis and prediction models for rail transit equipment. It has also engineered a fault detection and diagnosis system for train bearings and suspension systems, which has been demonstrated in real-world applications, providing strong technical support for enhancing train system reliability and evaluating operational service capability. The team has also developed a relay monitoring and testing platform for railway vehicles, which has been deployed and put into production use on the Beijing Subway.

II. Team Member Profiles
Xiu-Kun Wei is a Professor and Doctoral Supervisor at the School of Traffic and Transportation, serving as an Editorial Board Member of the journal Control and Decision and a member of the International Program Committee of the Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). She is also a committee member of the Rail Transit Electrical Equipment Technology Professional Committee under the China Electrotechnical Society. Her primary research focus lies in rail transit inspection technologies. She is dedicated to advancing scientific and technological progress and cultivating high-level talent in this field. Under her leadership, the team has published more than 20 high-quality research papers in top-tier international journals such as Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence and IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Her research achievements have been recognized with two provincial/ministerial-level Science and Technology Progress Awards and two industry/association awards. Prof. Wei has participated in and led numerous national, provincial, and ministerial-level research projects, accumulating over RMB 10 million in research funding. As the first inventor, she has been granted more than 20 patents, covering multiple critical areas within rail transit inspection technologies. In addition, the research team includes over 10 doctoral and master’s students, forming a dynamic and innovative research group committed to advancing intelligent rail transit inspection.
III. Research Achievements (Video: Click to Play)
3.1 Representative Publications
| Paper Title |
Journal |
Time |
|
Subtle defect detection on the surface of railway PCCS based on deep learning
|
MEASUREMENT
|
2024
|
|
RTLSeg: A novel multi-component inspection network for railway track line based on instance segmentation
|
ENGINEERING APPLICATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
|
2023
|
|
High Precision Robust Real-Time Lightweight Approach for Railway Pantograph Slider Wear Estimation
|
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS
|
2023
|
|
A survey of the application of machine vision in rail transit system inspection [机器视觉在轨道交通系统状态检测中的应用综述]
|
Control and Decisio |
2021
|
|
Multi-Target Defect Identification for Railway Track Line Based on Image Processing and Improved YOLOv3 Model
|
IEEE ACCESS
|
2020
|
|
Squats and corrugation detection of railway track based on time-frequency analysis by using bogie acceleration measurements
|
VEHICLE SYSTEM DYNAMICS
|
2020
|
|
Wear analysis and prediction of rigid catenary contact wire and pantograph strip for railway system
|
WEAR
|
2020
|
|
Railway track fastener defect detection based on image processing and deep learning techniques: A comparative study
|
ENGINEERING APPLICATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
|
2019
|
|
Defect Detection of Pantograph Slide Based on Deep Learning and Image Processing Technology
|
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS
|
2020
|
|
Urban rail track condition monitoring based on in-service vehicle acceleration measurements
|
MEASUREMENT
|
2016
|
3.2 Representative Monographs
| Title of work |
publishing house
|
Publication time |
| Optimization and prediction technology of maintenance strategy for subway vehicles and power supply systems |
Electronic Industry Press |
2024
|
| Intercity EMU system repair and maintenance strategy |
Southwest Jiaotong University Press |
2022
|
| Deep learning-based subway infrastructure disease detection |
Science Press |
2021
|
| modeling and predictive maintenance strategy of subway driving equipment service capacity |
Science Press |
2021
|
|
Modeling and reliability analysis of the service capacity of mechanical and electrical equipment in subway stations
|
Science Press
|
2021
|
| Dynamic detection of modern railway track irregularities and diseases |
Science Press |
2017
|
| Fault diagnosis of rail transit train bearing and suspension system |
People's Transportation Publishing House
|
2015
|
3.3 Representative Research Projects
| Project name |
Project Source |
Project time
|
| Research on intelligent monitoring, early warning and operation and maintenance support technology in transit |
Ministry of Science and Technology "Science and Technology Support" |
2015-2017
|
| Research on a new mode of intensive maintenance of rail transit network in megacities |
National Key R&D Program - Tasks |
2020-2023
|
| Research on the deterioration mechanism of material performance, service capacity modeling and line detection technology of driving equipment in complex environments |
National Key R&D Program
|
2017-2020
|
| Research and demonstration of urban rail station equipment and material performance deterioration mechanism, service capacity modeling and station guidance traffic capacity improvement technology |
National Key R&D Program |
2017-2020
|
| R&D of vehicle-ground integration over-the-horizon collaborative perception and safety assurance equipment and systems |
National Key R&D Program - Topic |
2023-2028
|
| Research on online intelligent health detection technology of high-speed maglev train based on image recognition technology |
National Key R&D Program - Tasks |
2024-2027
|
| Research on the core element set of freight train operation behavior evaluation, the relationship between elements and the advanced optimization energy-saving algorithm |
Ministry of Science and Technology "Science and Technology Support" |
2013-2016
|
3.4 Representative Intellectual Property
| Patent Name |
Patent number |
Time |
| Prediction method of remaining life of vehicle bearings based on Wiener process with measurement error |
ZL202111142187.5
|
2021
|
| Pantograph carbon skateboard wear estimation method and device based on image segmentation |
ZL202210973857.6
|
2022
|
| Acquisition method of optimal maintenance strategy of rail transit on-board signaling system |
ZL202010240479.1
|
2020
|
| Prediction method of vehicle bearing remaining life based on multi-eigenquantity correlation vector machine |
ZL202010017661.0
|
2020
|
| Estimation method of wave abrasion wavelength and wave depth of inner rail of small radius curve of rail |
ZL202010207617.6
|
2020
|
3.5 Representative Awards and Honors
| Name of the winning project |
Award Name |
Award time |
| Development of key technologies and systems for holographic mobile detection and operation and maintenance of urban rail transit infrastructure |
Second Prize of Shanghai Science and Technology Award
|
2015
|
| Research and demonstration application of next-generation subway vehicle technology |
Second prize of Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Award
|
2021
|
| Key technologies and applications of active safety assurance for high-speed trains and urban rail trains |
The 9th International Invention Exhibition "Invention and Entrepreneurship Award" Gold Award |
2016
|
| Key technologies and applications of high-speed train in-transit status perception early warning and operation and maintenance support |
First Prize of Science and Technology Award
|
2018
|
| Review of the Application of Machine Vision in Rail Transit System State Detection, Vol. 36, No. 2, 2021 |
"Control and Decision" 2021 (Academic Hotspot) Best Paper |
2022
|
3.6 Representative Application Demonstrations
The team has successfully implemented a series of intelligent inspection and monitoring systems in real-world rail transit scenarios, showcasing the practical value and engineering maturity of its research outcomes. Key application demonstrations include:
(1) Intrusion Object Detection on Railway Tracks
Detects obstacles within the railway clearance zone that may endanger train operation—such as rocks, pedestrians, or debris. Leveraging deep learning and computer vision technologies, the system identifies and localizes intrusions in real time, enabling early perception, early judgment, and early warning, thereby preventing major accidents and ensuring operational safety.
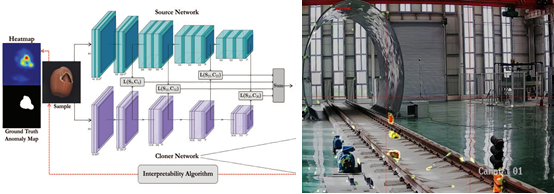
(2) Urban Rail Train Driver Behavior Monitoring
Addresses the limitation of manual observation in current driver gesture monitoring by proposing an automatic, real-time gesture recognition method based on cab surveillance video. Using deep learning techniques—including object detection and human pose estimation—the system achieves high accuracy and strong real-time performance in identifying critical driver hand signals.

(3) Multi-Label Weather Recognition for Rail Environments
A fine-grained weather classification model is built using multi-level feature fusion and attention mechanisms, enhancing semantic representation of environmental images. The system efficiently recognizes multiple concurrent weather conditions (e.g., sunny, cloudy, rainy) to support real-time environmental safety monitoring and early warning in rail operations.

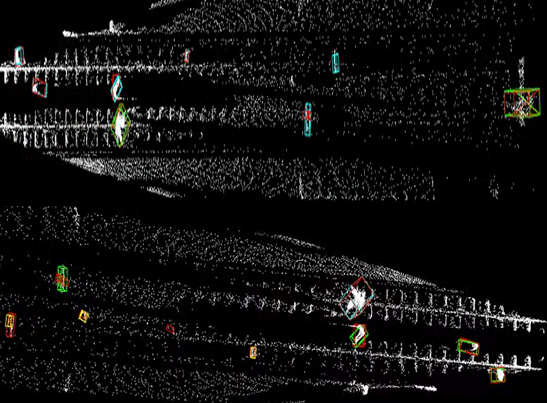
(4) LiDAR-Based Obstacle Detection for Railways
Utilizes 3D point cloud data from LiDAR sensors to detect obstacles ahead of moving trains. By training deep learning networks on this spatial data, the system accurately predicts the position, size, and shape of hazardous objects, enabling proactive collision avoidance through timely warnings.

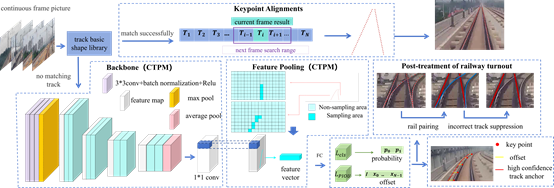
(5) Track Line Detection
Employs deep learning and image processing techniques to detect and localize tracks ahead of the train. Accurate track identification helps define the high-speed rail clearance boundary, supports precise spatial localization, and significantly enhances the train’s environmental perception capability.
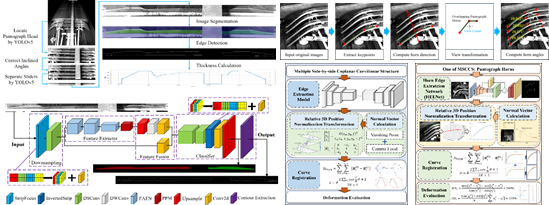
(6) High-Precision Inspection of Pantographs
Monitors the real-time safety status and key geometric parameters (e.g., height, offset, wear) of pantographs in rail transit systems. Based on machine vision and deep learning, the system enables automated, high-accuracy measurement and structural assessment, improving the intelligence and efficiency of maintenance operations.
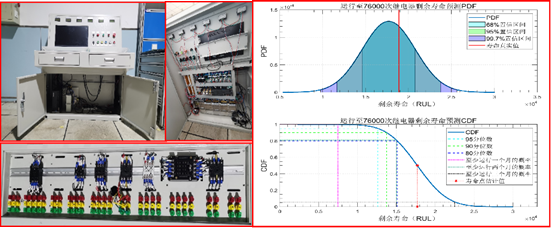
(7) Intelligent Predictive Maintenance System for Relays – Application Demonstration
A dedicated predictive maintenance platform for train relays has been deployed. The system collects time-domain and electrical parameters of relays and applies Wiener process modeling, Gaussian Process Regression (GPR), and Dempster–Shafer evidence theory to assess health status and predict remaining useful life. This system has been put into production use on the Beijing Subway.
(8) Condition Monitoring Demonstration for 600 km/h High-Speed Maglev Critical Systems
Focuses on key subsystems of the 600 km/h high-speed maglev train. Through system decoupling, failure mechanism analysis, and characteristic parameter extraction, the team integrates physics-informed models with data-driven approaches and simulation-based digital twins to enable comprehensive health management.
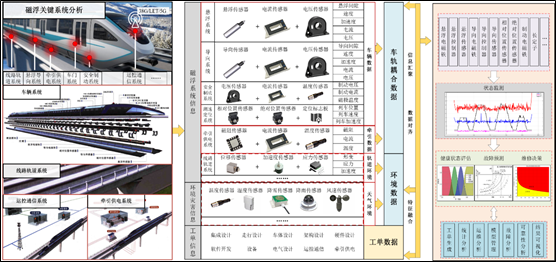
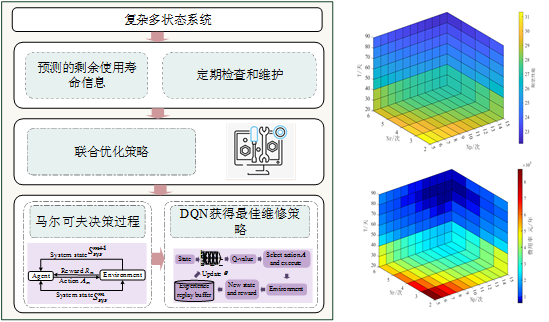
(9) Reliability Analysis and Maintenance Strategy Optimization
Develops degradation models based on failure theory, shock models, and Markov processes, and employs intelligent optimization algorithms and machine learning to analyze equipment reliability. The resulting framework supports the formulation and refinement of optimal maintenance strategies, ensuring safe, reliable, and cost-effective operation of rail transit systems.
IV. Team Contact Person and Contact Information
Contact Person: Prof. Xiu-Kun Wei
Email: xkwei@bjtu.edu.cn










